ElasticSearch ES核心概念
ES 概念
类比关系型数据库
通俗解释
Index
数据库
存储一类数据的集合,如“用户索引”
Document
表中的一行
一条具体的数据记录,格式为 JSON
Field
表中的列
数据的属性,如“姓名”、“年龄”
Mapping
表结构定义
定义字段的数据类型和属性
Shard
分区
将数据分片,便于分布式存储和查询
Replica
副本
数据的备份,提高容错性和查询性能
ES使用场景
我们在哪些场景下可以使用ES呢?
1)海量数据的分布式存储以及集群管理,达到了服务与数据的高可用以及水平扩展;
2)近实时搜索,性能卓越。对结构化、全文、地理位置等类型数据的处理;
3)海量数据的近实时分析(聚合功能)
1)网站搜索、垂直搜索、代码搜索;
2)日志管理与分析、安全指标监控、应用性能监控、Web抓取舆情分析;
ES架构设计
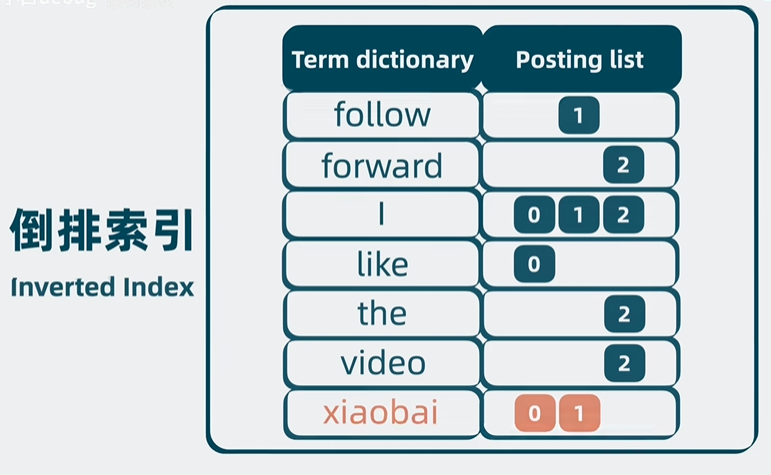
倒排索引
将词项拆分,按照字典排序,组成term dictionary,并将词项对应的信息,如文档id等对应放入另一侧,组成posting list
存放在磁盘中
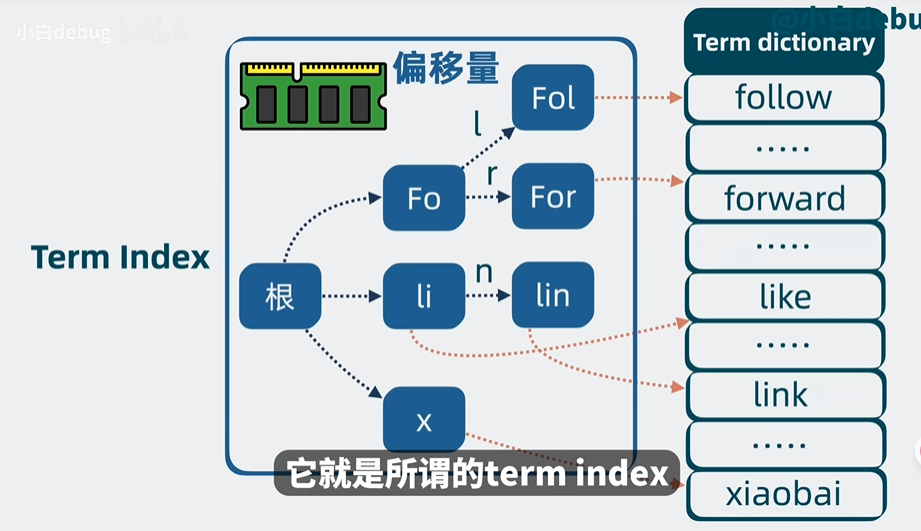
Term Index
前缀树,通过对term的前缀做树的搜索结合,加上与term dictionary的映射,将之放到内存中,进行检索加速
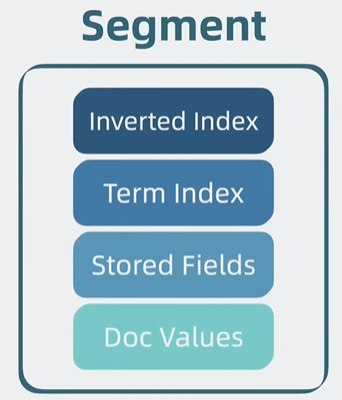
Stored Fields
用于存放文档的完整信息
Doc Values
用于排序和聚合
segment
以上四部分组合起来,构成一个可以搜索的最底层结构,称为segment
lucene
多个segment组合起来,segment生成后不可修改,老segment用于读,新segment用于写,不定期合并segment防止句柄耗尽,构成搜索库lucene
高性能
对写入lucene的数据进行分类,不同类数据写入不同lucene中。
每一类数据进行数据分片,形成shared,每个分片都是一个独立的lucene库
高扩展性
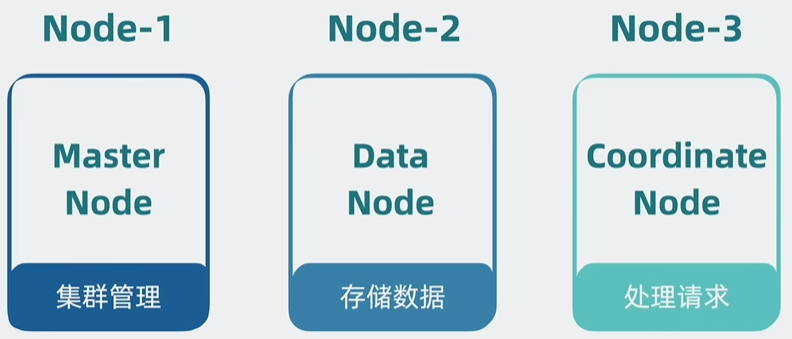
分片部署到不同机器上,每个机器就是一个node
高可用性
为分片添加副本,主分片数据同步给副本,副本对外提供读操作,并且在主分片挂的时候升格为主分片(类似主从)
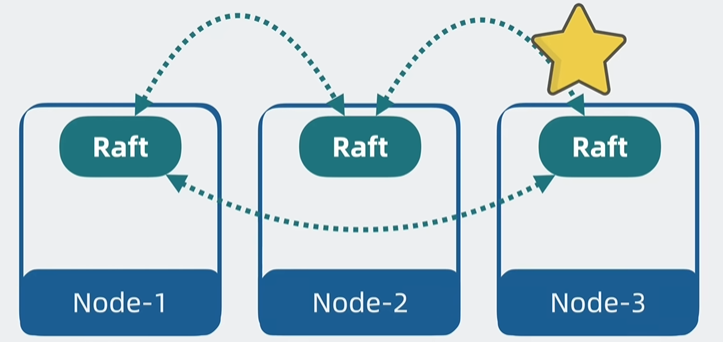
角色分化。不同node负责不同的功能
去中心化。每个节点引入魔改的Raft模块,保证不同node之间的数据一致性,同时可以了解其他node的健康状况,以便进行选主
ES配置 1 curl -fsSL https://elastic.co/start-local | sh
官方Go-SDK使用 连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 client, err := elasticsearch.NewTypedClient(elasticsearch.Config{string {"http://localhost:9200" },"elastic" ,"LUB7jymz" ,if err != nil {panic (err)
创建index
1 2 3 4 5 6 "first_try" ).Do(context.Background())if err != nil {"create index err:%v" , err)"Create Index Succefully" , res)
index里存储document
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 struct {string `json:"name"` "woodQQQ" ,"first_try" ).Id("1" ).Request(document).Do(context.Background())if err != nil {panic (err)"Index Document Succefully" , res)
通过id获取document
1 2 3 4 5 6 "first_try" , "1" ).Do(context.Background())if err != nil {"Get Document Succefully" , string (res.Source_))
搜索document
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "index_name" ).map [string ]types.MatchQuery{"name" : {Query: "Foo" },if err != nil {for _, hit := range res.Hits.Hits {string (hit.Source_))
更新document
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "first_try" , "1" ).Request(&update.Request{`{ "name" : "woodQ" }` ),if err != nil {
Typed-API使用 ✅ 0. 前提:创建 Typed Client 1 2 3 4 es, _ := elasticsearch.NewTypedClient(elasticsearch.Config{string {"http://localhost:9200" },
✅ 1. Match 查询:全文匹配(模糊搜索) 用于模糊匹配某个字段的内容(如搜索标题含 “go” 的文档):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 res, err := es.Search()."articles" ).map [string ]types.MatchQuery{"title" : {"golang" ,
✅ 2. Term 查询:精确匹配(适用于 keyword) 精确匹配字段值(非分析字段),如 status: "published":
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 res, err := es.Search()."articles" ).map [string ]types.TermQuery{"status" : {"published" ,
✅ 3. Bool 查询:组合多个条件(must、should、must_not) 复合查询常用于构建多个 AND/OR 条件组合:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 res, err := es.Search()."articles" ).map [string ]types.MatchQuery{"title" : {Query: "golang" },map [string ]types.TermQuery{"status" : {Value: "published" },
✅ 4. Range 查询:数值或日期范围 用于价格区间、时间范围、评分等:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 res, err := es.Search()."products" ).map [string ]types.RangeQuery{"price" : {100 ),300 ),
✅ 5. 聚合(Aggregation):统计分析 聚合可以统计数量、平均值、最大值等:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 res, err := es.Search()."sales" ).0 ), map [string ]types.Aggregations{"total_sales" : {"amount" ,"Sum result:" , res.Aggregations["total_sales" ].Sum.Value)
✅ 6. 分页 + 排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 res, err := es.Search()."articles" ).0 ),10 ),map [string ]types.SortOptionsValue{"created_at" : {
🔚 总结:Typed API 支持的常见查询手段
类型
用途示例
Match
模糊搜索(如标题、描述)
Term
精准匹配(如状态、分类 ID)
Bool
多条件组合查询
Range
日期、价格、数值区间
Aggregation
统计、分组、分析
Sort + Page
排序和分页
正确项目实操流程 ✅ 第一步:定义文档结构(对应 Elasticsearch 映射) 在 Go 中,先定义你要索引的文档结构体:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 type Article struct {string `json:"id,omitempty"` string `json:"title"` string `json:"author"` string `json:"tags,omitempty"` bool `json:"published"` `json:"created_at"`
✅ 第二步:创建索引 + 设置 Mapping(字段类型) 用 typed client 显式创建索引结构:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 res, err := es.Indices.Create("articles" ).map [string ]types.Property{"title" : types.NewTextProperty(),"author" : types.NewKeywordProperty(),"tags" : types.NewKeywordProperty(),"published" : types.NewBooleanProperty(),"created_at" : types.NewDateProperty(),if err != nil {"Index creation failed: %v" , err)
🔎 为何不自动创建?默认自动创建会使用默认 Mapping,容易出问题,比如 keyword 和 text 混用导致无法聚合、排序。
✅ 第三步:写入文档(Index) 将文档写入到上面创建的索引:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 doc := Article{"1" ,"Intro to Elasticsearch with Go" ,"Alice" ,string {"elasticsearch" , "go" },true ,"articles" ).
✅ 第四步:构建检索逻辑(Search) 查询作者为 Alice,标题中含 “go”的已发布文章:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 res, err := es.Search()."articles" ).map [string ]types.MatchQuery{"title" : {Query: "go" },map [string ]types.TermQuery{"author" : {Value: "Alice" },map [string ]types.TermQuery{"published" : {Value: true },map [string ]types.SortOptionsValue{"created_at" : {Order: types.SortOrderDesc.Ptr()},
✅ 第五步:解析检索结果 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 for _, hit := range res.Hits.Hits {var a Articleif err != nil {"Failed to unmarshal hit: %v" , err)continue "Found article: %+v\n" , a)
🧠 实践经验总结
阶段
建议
建索引
显式创建 mapping,明确哪些是 keyword(可聚合)哪些是 text(可搜索)
写文档
用结构体构建数据,防止 JSON 拼写错
搜索
统一用 typedapi/types.Query 构建,避免拼 JSON
结果解析
json.Unmarshal(hit.Source_, &obj) 是标准方式
测试 & 调试
用 Kibana 或 curl 先确认查询逻辑,再迁移到 typed client
ES自带的向量检索方案
Script Score的精确检索dense_vector 字段中,然后在查询时通过脚本(Painless)计算查询向量与文档向量的相似度(常见指标有余弦相似度、欧氏距离、点积等)
优点:无须预先构建索引
缺点:脚本计算的开销会变大
KNN的近似最近邻检索
原理:在文档索引阶段,通过向量插入建立 HNSW 图(类似于图结构,每个节点是一个向量,图中的边链接相似向量)
查询时,起始于图中的某几个入口节点,向下逐层搜索与查询向量相似的节点,并逐步收敛到最接近的近邻。
优点:高吞吐,高性能,查询速度快
缺点:资源占用大
混合检索hybird search
先对某些字段过滤,过滤后做向量相似度检索